How To Find Ip Address Of Device Connected Via Ethernet
Amid predictions that 75.44 billion devices will have internet connectivity by 2025, IP address management has become a key housekeeping and security business concern for whatever networking admin. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to endow more and more devices with smart capabilities, networking grows more complex, making IP-centered network security measures a business organization imperative. With more devices comes more than risk of networking complications and potential breaches—specially given the BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) trend, which allows employees to connect to company Wi-Fi via their personal mobile phones and laptops.
To maintain good network health and preclude unauthorized users from spying or wasting valuable bandwidth, admins are expected to not only know how to scan their network for devices just also sympathize the importance backside IP address management.
With the number of networked devices skyrocketing, network administrators must know how to scan their network for devices, track IP addresses, and perform IP address direction. This guide describes how IP accost scanners help empower It departments to amend track the many devices within a network, identify when IP addresses have been mislabeled or misallocated, and notice possible breaches, in addition to diving deeper into the why and how of IP accost direction from answering basic to advanced IP address strategies.
- How to Find All IP Addresses on a Network
- All-time IP Scanners
- The Importance of IP Addresses in Networking
- What Is an IP?
- What Version Is My IP Address? IPv4 vs. IPv6
- What Is IPv4?
- IPv4 Classful Addressing Nuts
- Classful vs. Classless Addressing
- What Is IPv6?
- How to Assign IP Addresses
- Positioning Your Organization for Success
How to Detect All IP Addresses on a Network
Knowing how to scan the network for devices is the first footstep, and one of the most fundamental, in managing IP addresses. When organizational members experience problems connecting their device to the network or the cyberspace, having a total list of IP addresses on the network can guide administrators every bit they troubleshoot and restore social club.
The virtually basic way to find all the IP addresses on a network is with a manual network scan. This method is best for those looking to perform a rapid, ane-time device check or for those heading smaller organizations with a more manageable device list. To speedily scan a network yourself using native operating organization (OS) capabilities, follow these steps.
- Open up the control prompt.
- Enter the command "ipconfig" for Mac or "ifconfig" on Linux. Your computer will then display its own IP address, subnet mask, gateway accost, and more than, making information technology possible for y'all to determine the network number yous'll be scanning. For example, in a Form C IPv4 network—which most minor local networks are wont to exist—you may discover your estimator's IP address is, let'southward say, 192.168.1.75. If the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, then you know the beginning iii bytes are the network ID (192.168.1) and your circulate IP address is 192.168.1.255.
- Next, input the command "arp -a". ARP stands for "Address Resolution Protocol," and the "-a" appendage of the command prompts the device to list all the IP addresses constitute inside the ARP cache for the associated network. In other words, the "arp -a" command displays all active IP addresses connected to the local network. This list is incredibly informative, containing the IP addresses, MAC addresses, and allocation type (whether static or dynamic) for all live hosts.
- Optional: Input the command "ping -t". The "ping -t" control allows you lot to perform an extended ping on the list produced by the previous command, testing connectivity and latency within the network. This will enable you to further narrow down what devices could be experiencing or causing issues.
Still, there are a few ways to browse local networks for IP addresses. Typically, the best way to find the IP addresses of all devices on a network is to invest in software. This is especially true for big organizations using dynamic IP addresses, in which case the large volume of networked devices and staggered accost changes can apace get overwhelming to rail and organize. Using an IP address scanner, admins can run into which addresses are active, which are complimentary for reallocation, which might belong to unauthorized users, and which take possibly been duplicated and caused collisions.
Dorsum to Top
Best IP Scanners
While it's possible to scan a network for active IP addresses using native commands, manually tracking the addresses of all networked devices can chop-chop become an outsized task for whatever one staff member. This is particularly truthful when you look at the data this method makes available to you. Aye, ipconfig displays the IP address of each active network device and its corresponding MAC address, but nigh Information technology members don't happen to know the MAC accost of every single computer within the network—that expectation would be unreasonable, if not impossible in larger networks. Suffice it to say, this information doesn't exactly guide you to the root source of a problem or provide much network mapping. It just enables you to identify IP addresses and spot possible duplicates or mismatches.
For this reason, downloading software with a fuller suite of IP address management (IPAM) services is highly recommended. To assistance you fill out your IPAM toolset, I've rounded upwards the seven best network scanner and address management clients. While some are gratuitous, these are by and large more than supplementary tools. Cobbled together, a collection of standalone software can certainly yield powerful results.
In terms of expedient and comprehensive data consolidation, however, the all-time results tend to come up from premium software. A completely integrated direction tool—similar the SolarWinds® IP Address Manager, the most robust IPAM software and my personal favorite—might have a higher price tag just ultimately pays for itself by automating rote tasks and performing insightful assay, decreasing system reanimation while increasing productivity and profit.
With that said, I'll review free tools first earlier delving into full-service clients.
one. IP Address Tracker (Free)
By far the near powerful tool on the list of free clients, SolarWinds IP Accost Tracker is a standalone solution, available for complimentary download, that works on its own but is further enhanced by the SolarWinds IPAM suite when integrated. This makes information technology an excellent kickoff pace if you lot're considering a premium option but looking for a fully functional address tracker in the meantime.
![]()
For a free tool, SolarWinds IP Address Tracker is extraordinary: not merely does it allow users to manage up to 254 IP addresses, just it automatically pushes alerts when IP address conflicts occur. What'due south more, information technology creates a repository of all IP addresses on a network, tracks subnets, and shows which addresses are bachelor.
Finally, its graphical user interface displays information in an intuitive and digestible format, highlighting notable events while remaining comprehensive in nature. For example, it shows a list of custom reports, the last 25 IPAM events, current conflicts, and ranked subnets by the percentage of available addresses used.
2. Angry IP Scanner (Free)
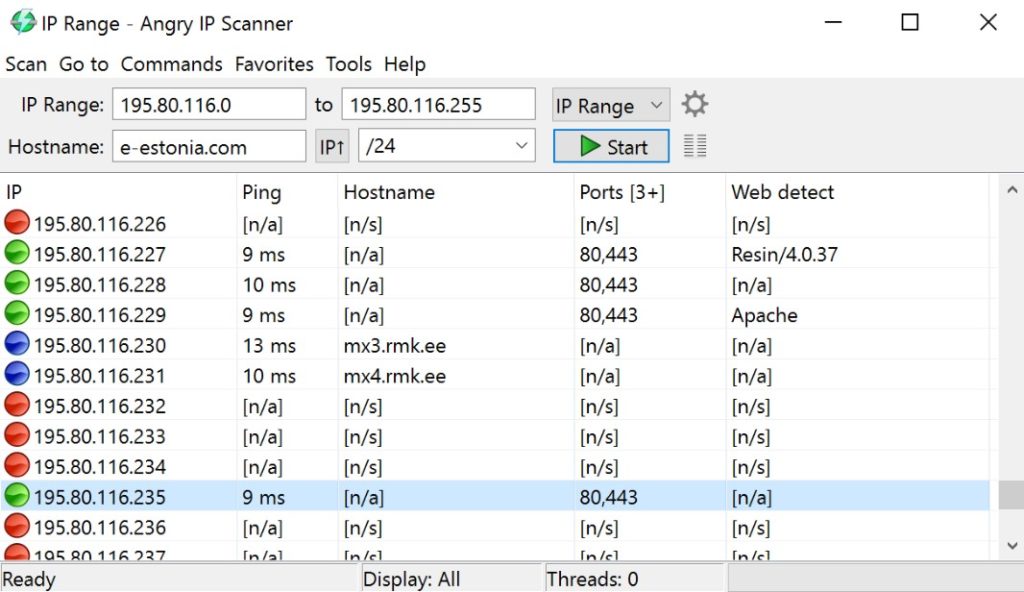
Widely hailed as i of the first and nigh popular free IP address scanners, Aroused IP Scanner is open up-source software, deployable across operating systems. Windows, Linux, and Mac Os X users will notice this tool handy for its nonexistent price tag.
Angry IP Scanner is easy to use and has an intuitive graphical user interface. Further, it provides slightly more detail than the manual command-line method covered to a higher place. Given an IP accost range, the tool displays all active IP addresses, hostname when applicable, ping response fourth dimension, MAC accost, and port count. These results are made actionable with an export office that supports CSV, TXT, XML, and IP-Port listing files.
Additionally, Angry IP Scanner tin brandish Network Bones Input/Output Organisation (NetBIOS) information useful for identifying an IP address, as knowing the computer name or current logged-in user tin can facilitate network problem solving.
The main downside of Angry IP Scanner is the basic nature of its capabilities, which is understandable given that it's open up-source. The functionalities it offers are fundamental and useful. Plus, anyone who writes Java is free to expand its abilities by creating their own plugins, though of form this would crave a certain corporeality of buy-in.
3. IP Scanner (Free)
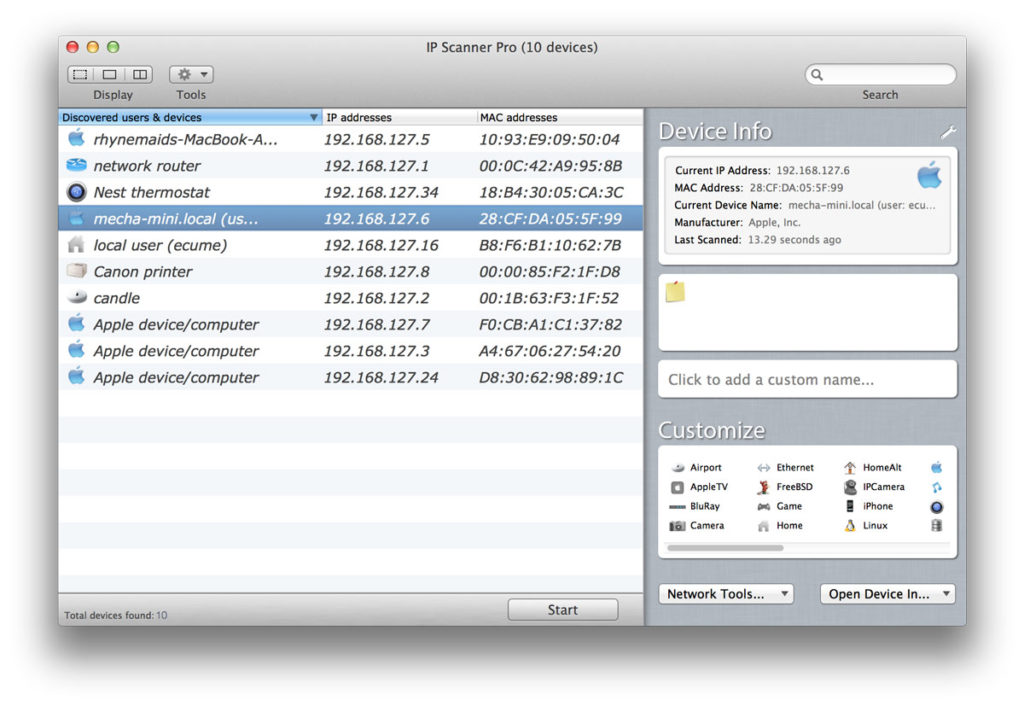
Created past programmer 10base-t Interactive and optimized for Mac, this app is admittedly limited; the gratuitous version only supports 6 devices. Nonetheless, for small-scale abode networks, this number may be sufficient, and, as a gustation of what could be possible with the expanded capacity of the Pro version, IP Scanner offers features many other free apps don't have.
Peradventure about interesting is IP Scanner's "cumulative manner" characteristic, which allows the user to rails network changes over time. In this mode, network admins tin can see inactive devices that were once part of the network. This can help with troubleshooting in a variety of ways. Is this IP address now free for reallocation? Is this device supposed to be present, and something has gone wrong? IP Scanner takes some of the guesswork out of network fluctuations, making it possible to zero in on these questions and detect answers.
Another intelligent feature is the tool's whitelist adequacy, which allows users to filter out trusted devices. By culling the display in this manner, users can stay aware of which devices are new and may exist on the network without say-so, receiving automatic alerts to potential threats.
4. IP Address Manager
The preeminent total-service IP address management tool, SolarWinds IPAM goes far across the offerings of an IP address tracker. In add-on to all the SolarWinds IP Address Tracker features covered above, IPAM is a complete management solution, empowering admins to drill down into address conflicts, easily classify IP addresses to subnets, and catalogue IP address usage history.
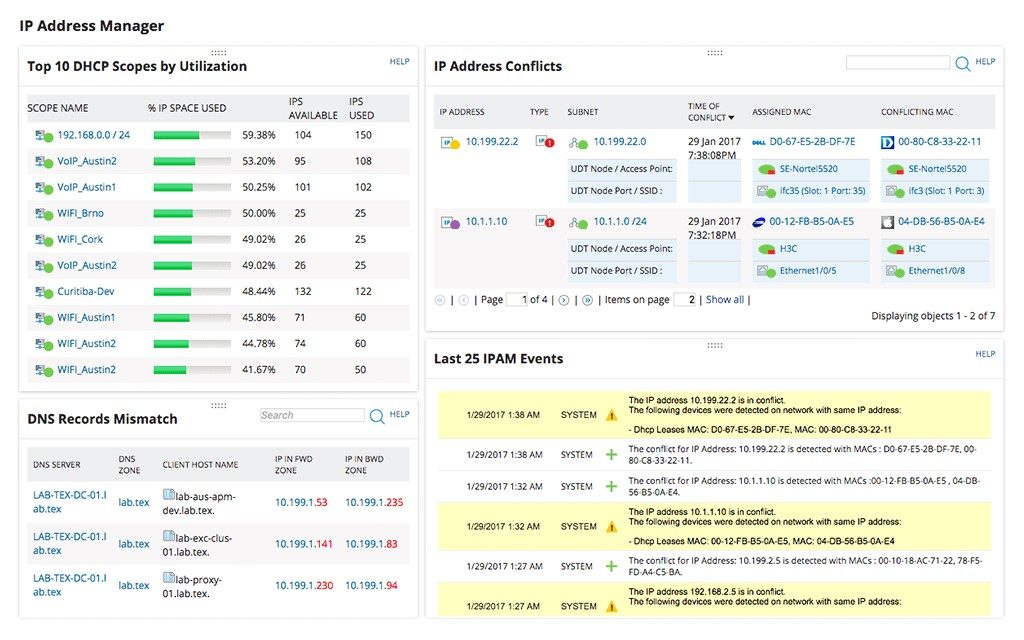
These functions are crucial time-savers. When alerted to a conflict, users can begin troubleshooting past viewing the event'southward details, including the specific endpoints involved. This allows admins to temporarily remove the malfunctioning devices by remotely shutting downward a port, thus facilitating network reliability and high functioning while reconfiguring IP settings behind the conflict.
As regards address resource allotment, IPAM users can employ the automated Subnet Discovery Wizard and Subnet Resource allotment Wizard to sort IP addresses and grade optimally sized subnets, maximizing functioning while minimizing conflicts and wasted space. Better yet, IPAM features drag-and-drop and user-defined grouping, making portioning IP address space more convenient than ever before.
Ane concluding notable feature here is that it offers priceless server synchronization. This makes it possible non merely to gear up alerts for conflicts and put out fires as they arise, simply to prevent potentially expensive address conflicts to begin with. IPAM integrates DNS server and DHCP server management in one console and supports multiple vendors. This ways customers can notice available addresses, assign them, and update the DNS simultaneously, eliminating the possibility of misdirected traffic or duplication.
5. Engineer'due south Toolset
Adjacent upwards is SolarWinds Engineer'south Toolset™ (ETS), a packet of over 60 tools designed to discover, configure, monitor, and troubleshoot your network. This includes a slate of tools fulfilling the duties of an IP tracker or scanner, bolstered by myriad others in this holistic network management client.
Some of the toolset's fundamental strengths are its convenience and birds-center-view perspective of complex enterprise networks. SolarWinds ETS performs automatic network discovery, allowing it to undertake clear network visualization—a capability not found in most free tools. With the automated discovery, the toolset displays the network in its entirety, mapping out switch ports, relating MAC to IP addresses, and identifying equipment.
To this end, ETS generates powerfully informative graphics for all IPAM concerns. Not only does the Ping Sweep tool provide a quick rundown of which addresses are in apply and which are bachelor for assignment, but it likewise locates the DNS name corresponding to each IP address. Information technology supplements this data with graphs charting device response time.
Beyond scanning and mapping networks, Engineer's Toolset makes reconfiguring the network for optimal operation a breeze. The Subnet Calculator at one time scans subnets; generates the proper masks, size, range, and broadcast address of both classful and classless subnets; and acts equally an IP address tracker, continuously monitoring the addresses in use inside each subnet.
The DHCP Telescopic Monitor, meanwhile, monitors DHCP servers to push alerts when certain scopes are depression on addresses and quantifies the number of dynamic IP addresses within the network. This is an incredibly important function when re-architecting a network or trying to avoid downtime, as it gauges whether the network is due to run out of addresses before a verifiable shortage arrives.
Further, the DNS Audit tool maximizes IP address efficiency through its ability to run forrad and reverse DNS lookups to find any misalignment with host addresses and DNS records. This helps ensure if a device is using an IP address, the network reaps the rewards of having allocated that address.
Coupled with the innumerable other amenities of SolarWinds ETS, its network scanning and IP address tracking features go fifty-fifty further in preventing network ending, identifying problems early, ascertaining root causes, and executing quick resolutions.
6. Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds Network Functioning Monitor (NPM) is another fully loaded toolkit prepare to scan networks for devices. Its network device scanner tool automatically discovers network devices; beyond that, NPM creates visual displays that delineate the connections between devices — automatically populating maps that analyze network topology. This is especially helpful in the case of the dynamic IP address system, in which IP addresses (in improver to device count and relationship) are constantly in flux.
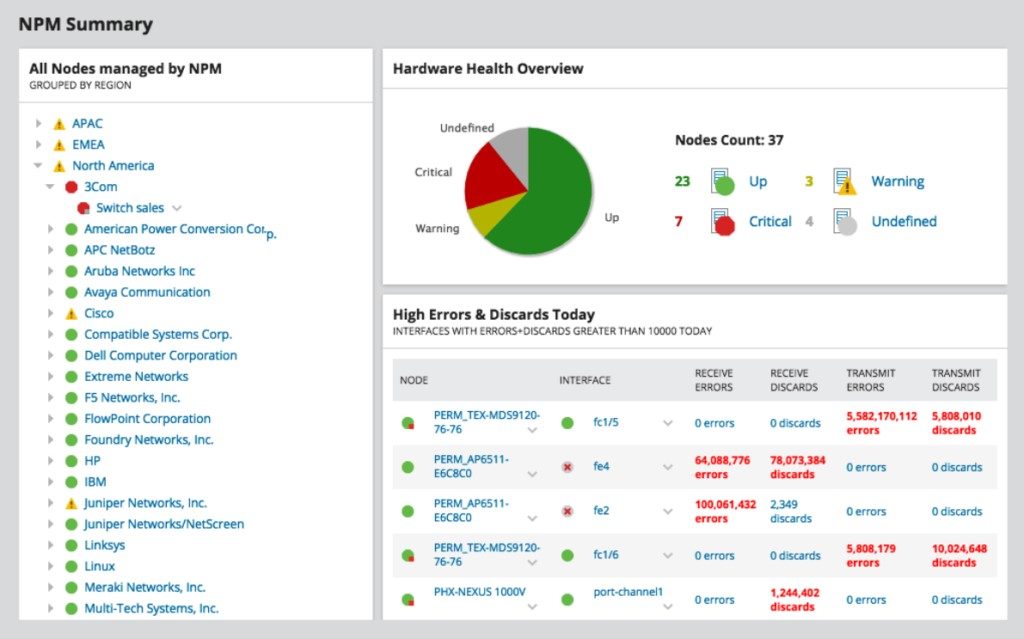
Network visualization in NPM goes far across the typical features of an IPAM tool. In fact, with SolarWinds NPM, users can customize dynamic network maps that display accurate topology and device performance metrics, juxtaposing device scanning and network performance management then that admins can more than hands architect high-performing networks and intervene on specific devices when necessary.
7. User Device Tracker
SolarWinds User Device Tracker (UDT) performs an IP address direction role from a unique vantage point, looking more than at the individual user in addition to network compages. UDT is invaluable when it comes to granular network topology and equipment details. It automatically discovers and monitors layer two and layer 3 switches, and information technology constantly watches ports and switches, gauging response time, packet loss, CPU load, and retention utilization. Information technology sends alerts as switches approach their chapters.
![]()
UDT serves a pragmatic function in this mode through network visualization and performance monitoring. In addition, it provides enhanced visibility into network users and strengthens network security—an increasingly crucial consideration as networks abound more complex and organizational members each bring a bevy of devices, presenting more opportunities for breaches.
With SolarWinds UDT, admins can not only customize their own reports—vital for compliance—but they can likewise drill into device connection history and user login history. Almost importantly, they tin can cut through the racket to identify any unauthorized users siphoning resources from their network or, worse, carrying out cyberattacks. The UDT whitelisting characteristic empowers admins to designate safe, known devices and so information technology can push alerts when new and potentially dangerous devices come up online.
Back to Top
The Importance of IP Addresses in Networking
At present that you have the best tool in identify to browse, monitor, and manage IP addresses on your network, having a baseline agreement of how IP addresses work—including the differences betwixt the addressing systems of IPv4 and IPv6—can as well help protect the functioning and integrity of networks. Permit's go into deeper particular about what exactly an IP address is, types of IP addresses, and how to assign IP addresses to devices.
What Is an IP?
The IP address exists to place devices connecting via the internet, which is itself a network of other networks communicating via the standards delineated past the Transfer Control Protocol (TCP) and Cyberspace Protocol (IP). The term "cyberspace" in this sense is dissimilar than Local Expanse Networks (LANs) in that it's decentralized—meaning no specific person or device has authoritative privileges to impose controls on the spider web—and allows each cyberspace-connected device to deed independently online.
To achieve internet admission, then, every device must accept a fashion of identifying itself. Identification serves 2 primary purposes:
- It acts as a "return address" and then all packets transmitted over TCP (all data transfers and communication exchanges, basically) tin be verified.
- It allows other devices to find and communicate with the device in question.
Though accessing the internet speedily and hands is something most take for granted, it's a process comprised of multiple steps. A user who wishes to achieve a site on a reckoner or other device inputs the domain name (like world wide web.dnsstuff.com) into their browser, which then contacts its designated domain name organisation (DNS) server to resolve the URL to an IP accost. Once the device has the IP address, it can connect to the site and interact yet it wants.
Because most networks, including LANs, virtual LANs, and Wide Area Networks (WANs), use the TCP/IP protocol suite to connect the devices in a given organization or location, the IP accost system works similarly to ensure network devices tin successfully transport data to one some other.
All IP addresses have both binary and dot-decimal notations for an address. The binary representation of an IP address is used to communicate with devices, while the translated dotted decimal format helps make it easier for users to sympathise and remember IP addresses.
Back to Top
What Version Is My IP Address? IPv4 vs. IPv6
Currently, there are two coexisting standards (also called versions) for formulating IP addresses:
- In IPv4 (Net Protocol version four), an IP address is made up of decimal digits and contains 32 bits or 4 bytes. Each byte constitutes an 8-bit field with decimals and a period, which is why some call IPv4 address nomenclature the "dot-decimal format."
While this has worked well plenty for quite some time, the 32-bit constraint ways IPv4 merely allows for variations or approximately 4 billion addresses. At nowadays, the global number of internet-connected devices already far exceeds that threshold, at 26.66 billion. To compensate, many networks utilize both private and public IP addresses, so several devices within a local network may share a public IP address but have separate private IP addresses. A arrangement called the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) assigns private IP addresses within a network.
While this system has worked historically, it poses a couple of bug. First, it introduces an boosted step in networking and increases authoritative overhead. Second, if the DHCP and DNS server aren't synchronized (or if multiple DHCPs are running at once, which admins should avoid), listed IP addresses tin can be wrong or duplicated, causing transfer issues that can, in turn, hinder network functioning. When two devices share a single IP address, they may non be able to connect to the internet or the local network at all.
- IPv6 was developed to circumvent these complications. Iv times larger than an IPv4 address, an IPv6 address contains 128 bits in total, written in hexadecimal, and punctuated past colons rather than periods.
With more than data allocated for each accost, the IPv6 protocol creates many more IP address variations than IPv4, eliminating the need to assign public and private addresses, which can outcome in collisions. Since it allows for variations, the new protocol provides a good deal of room for IoT to grow.
Because IPv6 is an evolutionary upgrade, information technology can coexist with IPv4 and will do so until the earlier version is eventually phased out. For this reason, IPv6 is also referred to as IPng — significant "Internet Protocol next generation."
So far, IPv6 addresses nevertheless represent the minority of net traffic, only they've started to capture a larger portion. As of June 2019, around 29% of Google users accessed the site over IPv6, and effectually 38% of internet users in the United States have already adopted IPv6 with minimal latency rates. By transitioning to IPv6 over fourth dimension, the internet should be able to allocate more individual addresses to devices, increasing both the number of hosts and the book of information traffic information technology can arrange.
Back to Summit
What Is IPv4?
Each IPv4 accost contains two crucial components: a network identifier and a host identifier. In this way, it'south much like a geographic address—the street gives people an idea of the neighborhood where a building is located, and the number isolates the building in question.
In an IPv4 address, the network identifier contains the network number, which, per its proper name, identifies the specific network to which the device belongs. The host identifier, or node identifier, is the collection of bits unique to the device in utilize on the network, differentiating it from other machines on the network and on the internet.
Back to Tiptop
IPv4 Classful Addressing Nuts
The number of nodes a network will need to support determines the verbal structure of the IPv4 address, which is further classified into dissimilar address classes.
- Grade A IPv4 addresses – If the first bit of an IPv4 binary accost is 0, so the address is a Grade A type. Class A is typically used in large organizations as information technology can generate millions of unique node variations. Grade A has an IP accost range of 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
- Class B IPv4 addresses – If the first two bits are 10, the IPv4 accost is Grade B. Class B can produce tens of thousands of node address variants and is primarily used in medium-sized networks. Form B has an IP range of 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
- Class C IPv4 addresses – All Class C addresses start with 110. Since Class C IPv4 address allocates ane byte to the host identifier, this tier of IPv4 network tin can only support a maximum of 254 hosts. This is because a byte of data is equal to 8 bits, or 8 "binary digits." With a chip limited to representing either 0 or 1, an 8-bit piece of data allows for a maximum of (256) variations. However, the host identifier "0" is reserved for the IP address designated to the network, and 255 belongs to the IP accost designated to the broadcast address, leaving 254 network nodes for other devices. Grade C has an IP range of 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255
While Classes D and E also exist, Class D is used exclusively for multicasts and Class E not bachelor to the general public.
Back to Top
Classful vs. Classless Addressing
Because of fears that the classful IPv4 addressing system was also quickly using up available address variations, the Internet Engineering Task Forcefulness developed the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) system to let for network prefixes sized betwixt the 8-flake intervals instituted by classful networking. With CIDR, an IPv4 address doesn't have a set composition defined by its class; it can, yet, have a prefix (the portion specifying the network number or subnet ID) of arbitrary length. The size of this prefix determines the number of variations available to each network or subnetwork.
CIDR can work considering of the variable-length subnet masking (VLSM) technique. Put simply, the subnet mask expresses in dot-decimal IP form how many bits in the IPv4 address belong to the prefix. For case, a CIDR with a prefix length of iv (pregnant the network number is only iv bits, as opposed to a typical Class A length of eight) is, in binary, 11110000 00000000 00000000 00000000. The byte "11110000" numerically translates to 240, making this subnet mask accost 240.0.0.0. Given this subnet mask, an admin knows the network can support devices—much more a Form A IPv4 address.
According to CIDR notation, the length of the subnet mask (the number of bits used by the prefix) is expressed by a suffix composed of a slash and a number. So, given the IP address 192.168.1.0/24, a user would know the following:
- The prefix is 24 $.25, or 3 bytes, in length, making information technology a Class C IP address
- Therefore, the network can support upward to 254 devices
- The network accost is the first 3 blocks, or 192.168.one
- The IP address is 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000 in binary, translating to the subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Back to Top
What Is IPv6?
IPv6 addresses work in a similar fashion to IPv4 addresses, though they comprise more information. Each hexadecimal number requires 4 bits, and each cake consists of iv hexadecimals. Each IPv6 address contains eight blocks—128 $.25 total, which are, similar IPv4, divided into network and node components. The difference between the two versions is IPv6 addresses don't vary in composition; the network and node components are ever of equal length, at 64 bits each.
The showtime 64 bits correspond to the network component, laying out the global unicast accost (48 bits) followed by the subnet ID (16 bits). Essentially, this means that the starting time 3 bytes identify the network address used past cyberspace routing to reach the proper network, and the fourth byte (configured past network administrators themselves) routes any communications to the right internal subnet within the broader local network.
The last 64 bits brand upward the interface ID, which identifies the node within the network that internal network or external cyberspace communications must reach. The interface ID is generated from the media access command (MAC) address, given by network interface card manufacturers and stored in the device hardware.
Although IPv6 addresses don't take classes, the hexadecimals with which the address starts can inflect what type of network it is. Global addresses starting with "2001" are public, whereas link-local addresses starting with "fe80" and unique local addresses starting with "fc00::/viii" or "fd00::/8" tin channel communications internally, but not over the internet.
Ultimately, IPv6 incurs some inconveniences. Namely, infrastructure will have to transition between the protocol versions, and the addresses are significantly longer. Merely the protocol solves the most notable dilemma networking faces: a shortage of IP addresses.
With its expanded capacity to back up network nodes, IPv6 doesn't just offer "enough" addresses for now; indeed, it is equipped to generate more variations than we'll (hopefully) e'er need. The number is practically inconceivable in human terms. As i computer hobbyist puts it, that value (340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456) is equal to over 340 undecillion. Put some other mode, that amounts to 50 octillion IP addresses per man being, given a global population of 7.5 billion.
Back to Top
How to Assign IP Addresses
Finally, to round out our agreement, it'southward worth clarifying how IP addresses are assigned to devices, and how this can touch network operation. In that location are ii basic forms of IP accost: static and dynamic.
In a static system, an ambassador assigns the IP address and it doesn't change with server updates, router reboots, or website changes. This understandably has its pros and cons. A static IP address can exist relied upon to stay the same regardless of other infrastructure developments, significant IT admins will never come across a surprise when scanning for IP addresses. However, depending on the size of the network, the transmission resource allotment of all host IP addresses can crave a massive amount of time, tracking, and structuring. Especially given that static addresses tin become incompatible with a system in various ways, choosing to exclusively use static addresses is largely inefficient and inflexible.
All the same, in that location are several adept reasons to opt for the static IP address system. The process of assigning a static IP address is lengthy and complicated, so it typically requires a professional. This constraint makes static IP addresses more than suitable to a business environment, though they tin add benefits to dwelling house networks as well. Static IP addresses are helpful when:
- You lot desire to ensure a shared resources (like a printer or server) is always accessible to everyone on the network, no matter their device, past giving information technology an unchanging accost
- Y'all want to use devices incompatible with DHCP
- You desire to avert IP address duplications, which a faulty DHCP server can generate
- You want slightly improved network security and geolocation precision compared to a dynamic IP address system
Dynamic IP addresses, in dissimilarity, are assigned by the DHCP server, eliminating the demand for an admin to spend hours allocating addresses. Equally their name implies, dynamic IP addresses don't stay the same over time—the DHCP doles out IP addresses to devices on a temporary lease. This automates many of the more than irksome details of configuring an IP accost system: without administrative oversight, the DHCP server tin assign a unique IP address, a subnet mask, a gateway address, and other requisite reference information (like the address of the DNS server) to all devices.
The advantages of the DHCP arrangement are obvious: it reduces administrative overhead and scales with the environs. It has its disadvantages, as well, notably regarding the temporary nature of the dynamic IP address. Although the network client tin attempt to renew the same address repeatedly, its accost is not guaranteed. Particularly when it comes to remote work, attempts to gain access to a distant device or network can fail without knowledge of its electric current IP address.
Additionally, within networks primarily reliant on DHCP simply have divers a few static IP addresses for isolated devices, a DHCP server can generate a unique IP address that conflicts with an existing static 1, or the DNS and DHCP servers tin autumn out of sync, causing some sites and devices to become unreachable. These potential hiccups have solutions—altering the DHCP scope to exclude static addresses in use; irresolute DNS scavenging settings to ensure the server purges old records and updates its data—just they require foresight and boosted work.
Yet, barring slight complications, a dynamic IP address organization is the most reasonable solution for large-scale networks. While many enterprises may use a static IP accost with their router for remote networking or internet security purposes, DHCP is an efficient, useful organisation for node address designation overall.
Back to Top
Positioning Your Arrangement for Success
Overall, regardless of network size, downloading tools can showtime an IT section'due south workload. While gratuitous tools are skillful at treatment smaller tasks—like simply discovering active IP addresses and correlating them to MAC addresses—a diverse toolkit like those offered by SolarWinds IP Address Manager provides a comprehensive solution.
Whether you're maintaining the security of a small network or looking to manage networks at the enterprise calibration, the premium IP address direction solutions from SolarWinds add the virtually value of any tool on the market place. By performing data analysis, streamlining loftier volumes of data into insightful graphs, offering useful network visualization, and pushing security and IP address conflict alerts, SolarWinds software tin can help ensure networks remain in safe, peak-operation shape. Ultimately, through keeping tabs on the many rote and time-intensive tasks required by IP accost systems, these robust tools free upwards administrators to apply themselves elsewhere.
Source: https://www.dnsstuff.com/scan-network-for-device-ip-address
Posted by: gagnefloore45.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Ip Address Of Device Connected Via Ethernet"
Post a Comment